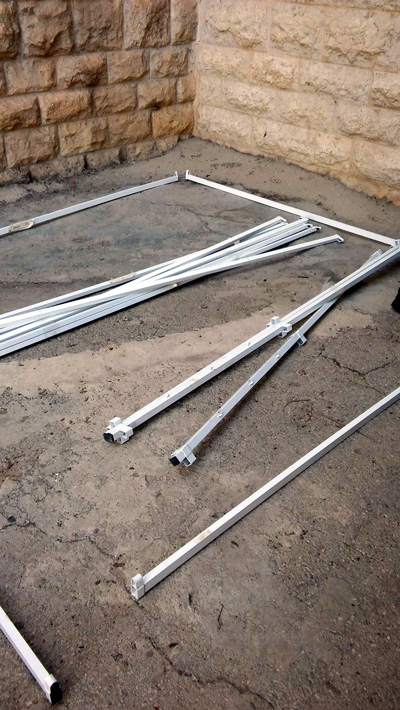
How to Bind the Lulav Bundle Guide for Sukkot The Ushpizin Holiday Havdalah 1) Start with laying the poles down An example of the wall. When you have the walls up wrap the walls with 3 rows of rope on the bottom of the walls. An example of the wall. When you have the walls up wrap the walls with 3 rows of rope on the bottom of the walls.Don’t forget to put away all the bags that the Sukkah parts were in. You will need then for Isru Chag-Sukkot. |
2) side poles snap into the columns. Don’t forget the center beam. The walls slide into the Top and Bottom Rows. Tie the walls to the frame tightly so that the wall will not move in the wind. 3) The walls slide into the Top and Bottom Rows. Tie the walls to the frame tightly so that the wall will not move in the wind. Next put the Bamboo poles on the top using plastic clips and put the schach on top of the Bamboo poles. 4) Next put the Bamboo poles on the top using plastic clips and put the schach on top of the Bamboo poles.5) When you have the walls up wrap the walls with 3 rows of rope on the bottom of the walls. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Safety tips for SukkotUnited Hatzalah emergency medics present safety guidelines for the upcoming Sukkot holiday, to prevent injuries during sukkah-building. The season for building Sukkot has just begun and United Hatzalah volunteers have already treated dozens of injuries that occurred while people were building Sukkot. The Spokesperson’s department has therefore issued a series of basic safety tips for the holiday. When building a Sukkah one should always be careful when standing or climbing in high places. It is recommended to use proper safety gloves so as to avoid injuries to the hands. Make sure that ladders are stable and being held by a second person. It is strongly recommended to work in pairs if not larger groups so that one person can ground the ladder properly and call emergency services should an accident occur. It is imperative to keep all nails, screws and tools away from the reach of small children. When lighting candles for Shabbat or the holidays, be sure to keep them in a safe location, not near flammable materials, out of the wind, and also out of the reach of small children. Keep the candles on a special platform that won’t burn such as a metal or glass tray and keep them away from the walls of the Sukkah or any flammable decorations. Eli Beer, Founder and President of United Hatzalah explained that: “In previous years United Hatzalah volunteers have treated dozens of injuries due to people falling off of ladders during the building and decorating of Sukkahs. Some of these instances, unfortunately, have resulted in fatalities and serious injuries. We ask the public to take extra care this year while building, residing in and taking down their Sukkahs. Our volunteers will be on hand at all times during the holiday to provide care for any and all who need it. We wish you and all of Israel a happy and healthy holiday.” |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Soldier’s Guide To Staying Outdoors |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
The UshpizinBy Yanki Tauber https://www.chabad.org/library/article_cdo/aid/4485/jewish/The-Ushpizin.htm Who and What Are the Ushpizin“Ushpizin” is Aramaic for “guests,” a reference to the seven supernal guests, “founding fathers” of the Jewish people, who come to visit us in the sukkah (the branch-covered hut in which we eat our meals throughout the festival of Sukkot), one for each of the seven days of the festival:
Translated into English, the word “ushpizin” loses some of its mystery and otherworldliness. Yet these “guests” are indeed quite mysterious (at least until we learn more about them) and otherworldly (at least until we make them part of ours). We use the Aramaic term because our source of information about these mystical guests is from the Zohar, the fundamental Kabbalistic work written in that mystical language. Sukkot GuestsGuests are an important part of the Jewish home all year round—there were even Jews who would never partake of a meal in their own home unless there was at least one guest, preferably a needy wayfarer, with whom to share it—but especially on Shabbat, and even more especially on the Jewish festivals (Passover, Shavuot, Sukkot, Rosh Hashanah, etc.). On the festivals, there is a special mitzvah (divine commandment),
“You shall rejoice on your festival” (Deuteronomy 16:14), and, our sages explain, the only true joy is shared joy. Indeed, the verse in full reads: “You shall rejoice in your festival—you, your son, your daughter, your manservant, your maidservant, the Levite, the stranger, the orphan and the widow who are within your cities.” In the words of Maimonides (Mishneh Torah, Laws of the Festivals 6:18): “When one eats and drinks, one must also feed the stranger, the orphan, the widow and other unfortunate paupers. But one who locks the doors of his courtyard, and eat and drinks with his children and wife but does not feed the poor and the embittered soul—this is not the joy of a mitzvah, but the joy of his belly . . .”
If guests are integral to festival joy, they are even more so to Sukkot. Sukkot is the festival of Jewish unity; in fact, the Talmud states that “it is fitting that all Jews should sit in one sukkah.”2 If this is logistically difficult to arrange, it should, at the very least, be implemented in principle. We cram as many guests as possible into our sukkah, demonstrating that we fully intend to implement the Jewish communal sukkah to the full extent of our ability, each in our own domain. There is even a story told about a certain chassidic master who, because he lacked a guest, the Patriarch Abraham refused to enter his sukkah (why Abraham was there—more on that later). The Kabbalah of the UshpizinAnd so we come to the ushpizin. As we fill our sukkah with earthly guests, we merit to host seven supernal guests. While all seven ushpizin visit our sukkah on each of the seven nights and days of Sukkot,3 each supernal “guest” is specifically associated with one of the festival’s seven days, and is the “leading” or dominant ushpiza for that night and day.4
The Kabbalists teach that these seven leaders—referred to in our tradition as the “seven shepherds of Israel”—correspond to the seven sefirot, or divine attributes, which categorize G‑d’s relationship with our reality, and which are mirrored in the seven basic components of our character (man having been created “in the image of G‑d”).
As each supernal “guest” graces our sukkah, he empowers us with the particular quality that defines him. This is the deeper reason that they are called the “shepherds of Israel,” for like a shepherd who provides nourishment for his flock, these seven leaders nourish us their spiritual essence: Abraham feeds us love; Isaac, self-discipline; Jacob, harmony and truth; and so on.
And while these seven great souls are our “shepherds” all year round, the seven days of Sukkot are a time when their presence in our lives is more pronounced and revealed. As we enter the “temporary dwelling” of the sukkah, freeing ourselves from the dependence we developed on the material comforts of home and hearth, we are now in a place in which our spiritual self is more revealed and accessible. In this place the ushpizin visit us, empowering us to connect the seven dimensions of our own soul’s “divine image” with its supernal source in the divine sefirot, feeding, nourishing and fortifying our spiritual self for the material year to come. The seven sefirot, or divine energies, we are fed by the ushpizin are:
Chronologically, the order would be: Abraham, Isaac, Jacob, Joseph, Moses, Aaron and David; in many communities, the ushpizin are welcomed into the sukkah in the order in which they historically lived upon our earth. However, when aligned with the supernal sefirot (divine attributes) which they embody and represent, Joseph, who represents the sefirah of yesod, follows Aaron, who represents hod. Talmud, Sukkah 27b. This can be compared with the fact that each sefirah incorporates within it elements of all seven. In the Jewish calendar, the day begins at nightfall and extends to the following evening. Thus, Shabbat begins Friday evening at sunset and ends at nightfall on Saturday; the same is the case with the festival. Thus, Abraham is the leading ushpiza for the first night of Sukkot and the day that follows, Isaac graces our sukkah on the second evening of the festival and on the following day, and so on. By Yanki Tauber |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
How to Bind the Lulav BundleChabad.org Staff https://www.chabad.org/library/article_cdo/aid/1019429/jewish/How-to-Bind-the-Lulav-Bundle.htm
In order to beautify the mitzvah, we fasten together the lulav, hadassim and aravot (palm frond, myrtle branches and willow branches). For those who’ve never done it before, binding the lulav can be a bit tricky. In most cases, your Four Kinds vendor will do this for you.
Though technically one can bind them together with any material, the custom is to use lulav leaves—thus no foreign substance will separate between the Four Kinds and the hands of the person fulfilling the mitzvah. There is no single universally followed way of tying the lulav. Different methods are employed in different communities. In most communities, the three kinds are bound together by way of a special holder woven of lulav leaves, which slides up the bottom of the lulav and has pockets for the hadassim and aravot. This holder is then securely tied to the lulav with a strip of lulav leaf. The hadassim should be placed in the pocket to the right of the person holding the lulav (as he will be shaking it on Sukkot), and the aravot to the left. The thickish green exterior of the lulav’s spine should be facing the person. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
It is customary to have three lulav-leaf ring ties around the lulav, symbolizing our three Patriarchs. As such, in addition to the ring with which the holder is fastened, (at least) another two rings are fastened around the lulav’s midsection. Chabad CustomChabad custom is to bind the lulav on the day prior to the holiday, while in the sukkah.
In addition, Chabad custom is not to use the woven holders, but rather to tie the hadassim and aravot directly to the bottom of the lulav using three lulav-leaf strips (all bound within the span of one handbreadth): |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
A lulav bound according to Chabad tradition. One aravah (willow branch) is placed on the right of the lulav (meaning, to the right of the person holding the lulav, as above) and one on the left. Then, one hadas (myrtle) is placed on the right of the lulav and one on the left (somewhat covering the aravot), and a third hadas is placed in middle—a bit towards the right side. Once these are all in place, they are all bound together with the three lulav strips.
(Many have the custom of using more than three hadassim. In 1991, the Rebbe suggested that everyone use at least six hadassim. The extra hadassim are just added to the mix.)
Then, in addition to the three lulav ties that hold together the three species, another two ties are fastened higher up, around the midsection of the lulav itself—with the lower one covered, at least partially, by the hadassim and aravot.
Notes:
By Chabad.org Staff © Copyright, all rights reserved. If you enjoyed this article, we encourage you to distribute it further, provided that you comply with Chabad.org’s copyright policy. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Hoshana Raba wish list Hoshana Raba; May Hashem grant you a wonderful year with all your heart’s wishes for the very best always! |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||

Guide for Sukkot“You shall dwell in booths for a seven-day period so that your generations will know that I caused the Children of Israel to dwell in booths when I took them.”Breslev Israel staff | Posted on 05September2023 https://breslev.com/259022/ “You shall dwell in booths for a seven-day period…So that your generations will know that I caused the Children of Israel to dwell in booths when I took them from the land of Egypt.” Overview of the HolidayOne of the three pilgrimage festivals that the Jewish people were commanded to celebrate each year is Sukkot – the Festival of Booths, which lasts a week from the 15th to the 21st of Tishrei (and in the Diaspora until the 22nd). The first day is a Yom Tov, and the rest of the 7 days are known as the Intermediate Days of the Festival. (A separate Festival –Shemini Atzeret or Simchat Torah – immediately follows Sukkot on the 8th day, the 22nd of Tishrei in Israel and on the 23rd in the Diaspora).
The source in the Torah is in Vayikra (23:34-35,41): “On the fifteenth day of this seventh month is the Festival of Booths, a seven day period for Hashem. On the first day is a holy convocation; you shall not do any laborious work…You shall celebrate it as a festival for Hashem, a seven-day period in the year, and eternal decree for your generations; in the seventh month shall you celebrate it.”
Dwelling in the sukkah (booth) is an integral part of the Festival. During the week we spend more time in the sukkah than in our house. It is an uplifting spiritual experience to live in the sukkah, and a quality family time as well.
The Sefer Chinuch (the Book of Education, which explains the 613 Mitzvot (Commandments) according to their Biblical source) writes concerning the mitzvah of dwelling in the sukkah: “One of the roots of the mitzvah is explicit in the Torah: In order that we should remember the great miracles that G-d made for our forefathers in the desert during the Exodus from Egypt. He surrounded them with the Clouds of Glory so the sun wouldn’t harm them in the day and the frost at night. Some explain that we commemorate the actual booths that the Children of Israel made in the desert.”
Even though the Exodus was in the month of Nissan, we weren’t commanded to make the sukkot in Nissan, because in the balmy days of Nissan farmers are accustomed to leave their homes and enjoy themselves in the shade of booths outdoors. It wouldn’t be so obvious that we are making the sukkah as a mitzvah of Hashem. During Tishrei, however, when the nights are cold and the rainy season is about to begin, farmers return to their homes. When we do the opposite, leaving our homes and dwelling in a sukkah, we are demonstrating that the purpose of the sukkah is the mitzvah of Hashem.
Sukkot falls in the harvest season, a time of plenty, when the farmer brings his produce into his silo. A man naturally feels haughty when he is wealthy, and thinks: “My strength and the might of my hand have made this wealth.” To counteract our tendency to arrogance the Torah commands us to leave our houses filled with the abundance of wealth in the harvest-time and to dwell in a sukkah. All a man needs for happiness is G-d’s protection symbolized by the sechach (the leafy covering over his head in the sukkah); even in the flimsy, temporary booth he can be full of joy in appreciation of what G-d has given him.
The Midrash says: “Why do we build the sukkah after Yom Kippur? Because on Rosh Hashanah G-d judges the entire world, and on Yom Kippur the judgment is sealed. Perhaps the Jewish people are obligated to go into exile? Therefore they make a sukkah and exile themselves from their homes to the sukkah.” Living in the SukkahThe sukkah should be made as beautiful as possible. Our Sages said: “Glorify Him with the mitzvot. Make a beautiful sukkah, beautiful lulav, etc. As it says: ‘This is my G-d and I will glorify Him…’” It’s a mitzvah for a person to attend to building the sukkah himself.
The Torah instructs us to live in the sukkah the way one would live in his home. The sukkah becomes his place of residence for the seven days of Sukkot. He should eat all his meals and entertain guests there. One should sleep in the sukkah even if he only needs to nap. Building the SukkahThe walls of the sukkah can be built from any material: wood, plastic, metal or stone; it must be sturdy enough to be immovable in an ordinary wind. For this reason, walls made of fabric are problematic and might render the entire sukkah as unkosher. The Dimensions of a SukkahA sukkah has at least three walls. The walls may not be elevated off the ground more than 3 tephachim (24 cm.) so that a small animal can’t crawl inside. The height must be more than 10 tephachim (80 cm.) but less than 20 ama (9.60 meters). The width of the walls must be at least seven tephachim (56 cm.). Sechach (Leafy “Roof”)After setting up the walls, one places the sechach (the leafy covering that provides shade) as the roof, using thin, narrow boards, placed horizontally on top of the walls to support it. Many people use tree branches, palm fronds, or bamboo; specially prepared bamboo mats are available. The principal explained in the Oral Law is that the sechach must be something which has the following characteristics:
A sukkah may not be built under tree branches that make shade over the sukkah. The amount of sechach should be enough that the shade provided by the sechach in the sukkah is more than the sunlight that passes through, but not so much that no stars can be seen at night through the sechach, or that rain could not penetrate The Four Species (“Arba Minim”)The Torah states (Vayikra 23): “You shall take for yourselves on the first day the fruit of a citron tree, the branches of date palms, twigs of a plaited tree, and brook willows; and you shall rejoice before Hashem your G-d seven days.”
The Sefer Chinuch (the Book of Education) says:
“One of the roots of this mitzvah is that a man is affected by the actions that he does continuously, his ideas and feelings follow his actions. Because G-d wanted to bring merit to His Chosen People, He gave them many mitzvot so they would be affected beneficially by performing them daily.
“The Festival is a time of joy for the Jewish people, since it’s the harvest season, when they bring the fruits of their labor into the home and people are naturally happy. G-d commanded them to make a Festival at that time, so they will have the merit that their joy and happiness can be dedicated to His Name. Joy may cause a person to be drawn after materialism and forget his fear of Heaven, so the Creator commanded His people to take items in their hands to remind them that all their joy should be dedicated to His Name and His honor. He wanted these reminders to be items that bring joy, just like the time of year, and it is well known that the four species are naturally endowed to bring joy to the heart of man when he gazes upon them.
“Furthermore, the four species resemble precious organs of a human being:
The mitzvah of the four species teaches us that we must seek to bring all the Jewish people closer to their Father in Heaven, no matter how distant they may be. We find in the Midrash that each one of the four species symbolizes a different type of Jew:
What does G-d do with them? To destroy them is unthinkable. Rather G-d says, ‘Bind them together in one bond and they will atone for each other.’”
The Midrash teaches us that even those that have no taste or scent – neither Torah nor good deeds – must not be distanced; rather we are to bind them together with the species that have a scent so they will absorb the good scent. In this way we must reach out to our estranged brothers and bring them close to the Torah scholars, who have both “taste and scent,” and the scholars will have good influence upon them until they come to resemble the Etrog themselves, possessing Torah and good deeds.
The mitzvah of the four species can only be fulfilled if all the four are held together simultaneously. The Jewish people are the same, even though we are so different from one another, we must always be unified. “You Shall Rejoice on Your Festival”On all Holidays we are commanded, “You shall rejoice on your Holiday,” but on Sukkot the joy is doubled and tripled, “And you shall be only joyous.” In our prayers we call the Festival of Sukkot “the time of our rejoicing.” We are enjoined to show our rejoicing by eating meat and drinking wine, wearing fine clothing, dancing, singing and laughter.
On the other Festivals we rejoice because of a specific historical event, such as the Exodus on Pesach or the Giving of the Torah on Shavuot. But on Sukkot, simcha (joy) is the essence of the Festival. Therefore the mitzvah to rejoice on Sukkot is very great. We must rejoice in truth, with all our heart. We rejoice that we have G-d, we’re happy for the connection we have with Him with all our being. We’re happy He cares for us like a father cares for his beloved child. Ushpizim – Exalted GuestsThe Zohar HaKadosh writes: “When the People of Israel leave their homes and enter the sukkah for the sake of G-d’s Name, they merit to welcome the Divine Presence there, and all the seven shepherds descend from Gan Eden and come to the sukkah as their guests.” The seven shepherds include the Patriarchs of the Jewish people who wandered from exile to exile and attained rest only after great toil and travail.
It is customary, upon entering the Sukkah, to invite the ushpizim to enter by reciting the traditional Aramaic formula contained in the prayer book:
Among the Sephardim, it is customary to prepare an ornate chair in the sukkah, which is covered with a fine cloth and upon which holy books are placed. The host declares: “This is the chair of the ushpizim.”
Since the sukkah is a dwelling for the Divine Presence and the exalted guests, it is proper that one also invite guests of flesh and blood, i.e., poor people, to share one’s meals in the sukkah, to please his Heavenly guests.
The sukkah is the dwelling place of the Divine Presence, so one must be careful not to speak meaningless conversation in the sukkah, certainly, even more so, he must avoid slander and gossip. Rather one should focus on words of Torah. One should behave in a very honorable way in the sukkah so as not to drive away the Divine Presence. Names of the FestivalThe Festival has a number of names:
The Pilgrimage to JerusalemSukkot is one of the three Festivals in which the Torah commands the People of Israel to go up to Jerusalem, to the Holy Temple, and to offer special sacrifices. The three Festivals are Pesach (Passover), Shavuot, and Sukkot. Today many are accustomed to visit the Western Wall in Jerusalem to commemorate this mitzvah.
The three Pilgrimage Festivals are connected to working the land:
Hoshana RabaThe Hoshana prayers are recited in the Synagogue each day of Sukkot as we circle the bima (lectern) holding the lulav and etrog. These prayers are for redemption, and are referred to as Hoshanot because each stanza of the prayer is accompanied by the word “hoshana” – a combination form of the words “hosha” and “na” – bring us salvation, please. The seventh day of Sukkot is called Hoshana Raba – literally, the great Hoshana, because on this day more Hoshana prayers are recited than any other day in Sukkot.
Hoshana Raba marks the day when the judgment, which begins on Rosh Hashanah, is sealed. At the beginning of the period, on Rosh Hashanah and Yom Kippur, the entire world passes before G-d in individual judgment. On Sukkot, the world is judged concerning water, fruit, and produce. The seventh day of the Festival, Hoshana Raba, is the day that this judgment is sealed. Because human life depends on water and all depends on the final decision, Hoshana Raba is invested with similarity to Yom Kippur and is marked by intense prayer and repentance.
We find in a Midrash: G-d said to Avraham: “I am one and you are one. I will grant your descendants one single day on which they can atone for their sins – Hoshana Raba.
The Mateh Moshe explains that G-d told Avraham that should Rosh Hashanah be insufficient to atone for their sins, then Yom Kippur will atone. And if Yom Kippur does not, then Hoshana Raba will.
Why was this promise made specifically to Avraham? Avraham’s light began to illuminate the world after twenty-one generations [counting from Adam]. Similarly, even if Israel’s light is late in shining, it will not be delayed for more than twenty-one days after Rosh Hashanah – i.e., on Hoshana Raba.
The custom is to remain awake all night on Hoshana Raba and to read from a special Tikkun. The essential character of the day is prayer and the awakening of Divine mercy at the time of the sealing of judgment and the issuing of “notes of decision” – the verdicts. This is the source of the custom of wishing one another a pitka tava – Aramaic for a “good note.”
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||

While most people put up sukkahs, police are taking them downTwo sukkahs, at least one of which had engineering permits, dismantled by police in Jerusalem.Arutz Sheva Staff, 19September2021 https://www.israelnationalnews.com/News/News.aspx/313737 The sukkah in Meah ShearimJerusalem municipality This year, however, police claimed that the sukkah lacked the requisite permits and that it posed a threat to the safety of the public. No objections were raised, and the sukkah was taken apart. The night before, however, an hours-long standoff resulted after over 200 police officers arrived in the Meah Shearim neighborhood of Jerusalem in order to dismantle the sukkah belonging to Rabbi Moshe Bransdorfer. This sukkah, too, has been built in the same fashion for years. It extends from a second-floor apartment and is supported on iron scaffolding, and according to accounts provided to Behadrey Haredim, it had been approved by none less than the Jerusalem Municipality’s own choice of engineer. Nonetheless, several private individuals and a medical clinic situated near the sukkah complained to police, who in turn claimed that the sukkah was a public hazard. “The sukkah was built on high scaffolding and posed a real risk to life and property, while harming passersby and the public using the medical center located there, which even filed a complaint to the municipality,” the police stated. The saga began last Tuesday, when police made their first visit to the sukkah and a spontaneous protest erupted. Eventually, Rabbi Bransdorfer came to an agreement with police and the municipality, according to which the sukkah would be dismantled by his family the next day. Apparently this did not occur, and the municipality then offered an alternative site for the sukkah. The offer was accepted, but then representatives of Rabbi Bransdorfer appealed to the court for a stay of execution of the demolition, which was not granted. The case was due to be heard in court on Sunday, but police decided to take action on the Saturday night preceding, and arrived in huge numbers, prepared for the fierce protests that indeed erupted. Police arrived with trucks and cranes, raided the adjacent building, evacuated everyone from the sukkah and the apartment, and then began to demolish the structure. According to attorney Shreiber, representing Rabbi Bransdorfer’s family, several of the claims made by those demanding the demolition are false, including a claim made by the health clinic that the sukkah blocked access to it, which is blatantly untrue as photographs showed. In addition, the sukkah obtained the approval of two engineers and was built according to the engineers’ instructions, including protective fencing placed around the scaffolding. “Every single year, engineers inspect the sukkah and the same was true this year,” one source told Behadrey Haredim. “The sukkah complied with the most stringent safety measures. But due to pressure from social media, the municipality decided to issue a demolition order regardless.” |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Holiday HavdalahBy Naftali Silberberg Holiday havdalah can be divided into two categories: 1) Havdalah recited at the conclusion of a holiday. 2) The special havdalah recited on a holiday which falls on Saturday night. Havdalah is made when entering a day of lesser holiness. Since Shabbat is holier than all the holidays, we recite the havdalah when Shabbat leads into a holiday. Following the same logic, havdalah is not recited if a holiday leads into Shabbat. Havdalah at the Conclusion of a Holiday
Havdalah is recited at the conclusion of the following biblical holidays: Rosh Hashanah; Yom Kippur; the first days of Sukkot; Simchat Torah; Passover, both its first and last days; and Shavuot. If the final day of the holiday was Shabbat, then the exact same havdalah procedure as a typical Saturday night is followed. If the holiday ended on another weeknight, the procedure is very similar to the Shabbat havdalah, but with some differences:
Havdalah From Shabbat to a Holiday (“Yaknahaz”)Whether a holiday begins on a Saturday night or if Saturday night ushers in the second day of a holiday, that night’s holiday kiddush incorporates within itself the havdalah for Shabbat as well. The whole text of the kiddush/havdalah can be found in your standard or holiday prayer book. The following is the basic procedure:
Note: There are many activities which are forbidden on Shabbat but permissible on a holiday. All such activities must wait until one verbally “separates” between Shabbat and the holiday. This, however, does not have to wait for kiddush/havdalah, as a special havdalah themed insert, the Vatodi’enu paragraph, is inserted in the Amidah of the night’s prayers. Alternatively, one can say: “Baruch hamavdil bayn kodesh likodesh” — “Blessed is the One who separates between (the) holiness (of Shabbat) and (the) holiness (of the holiday).” Rabbi Naftali Silberberg is a writer, editor and director of the curriculum department at the Rohr Jewish Learning Institute. Rabbi Silberberg resides in Brooklyn, New York, with his wife, Chaya Mushka, and their three children. Click to Enlarge |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||